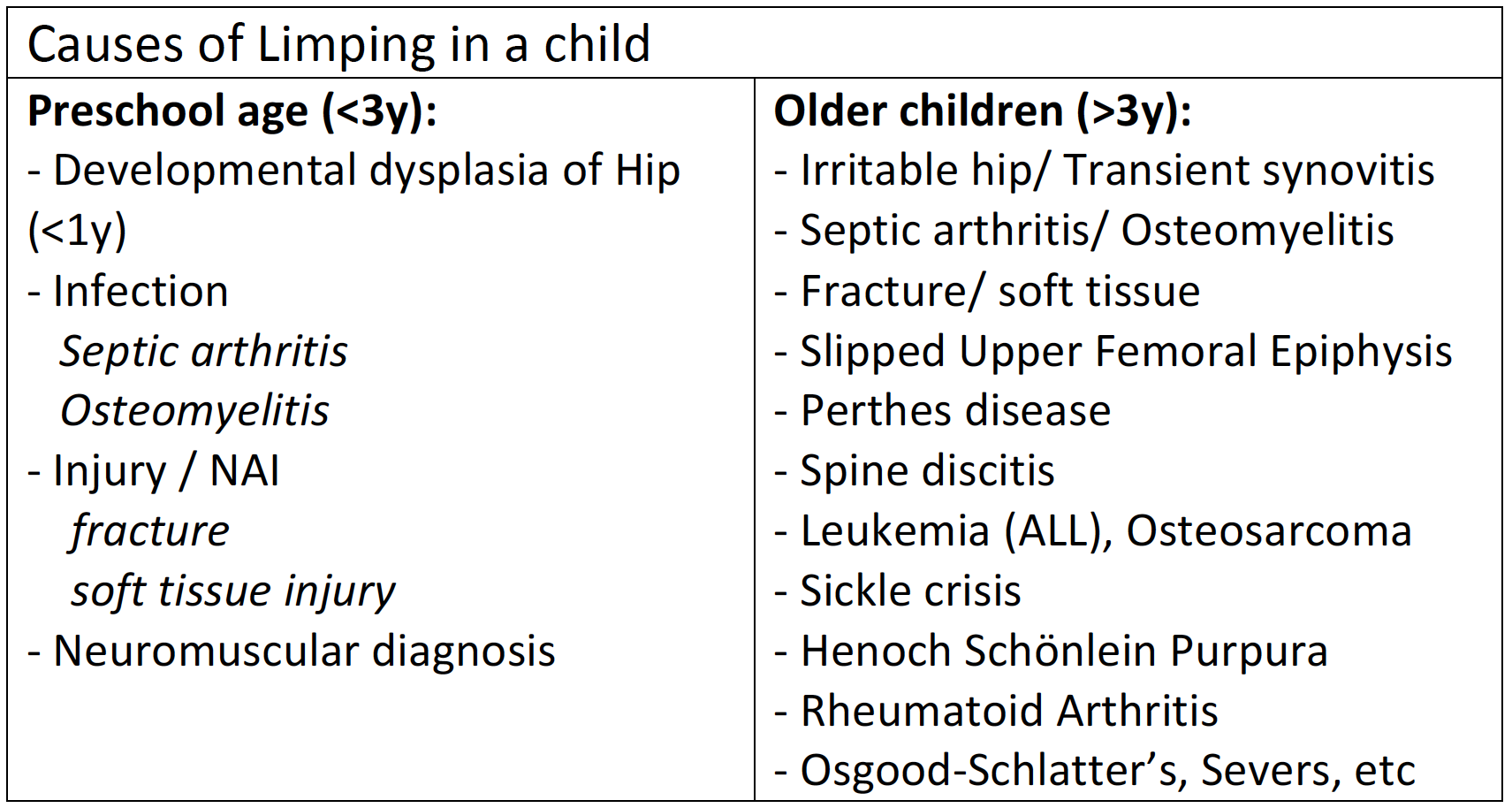
Limping child
There is a wide ranging clinical concern in children presenting with a limp from benign to sinister causes as follows:
History:
– Onset and duration of symptoms
– Presence of Fever?
– recent illness (e.g. URTI), Rash
– Any known trauma?
– Is child able to localise site of pain?
– Any joint swollen, red or warm?
– Pallor, tiredness, weightless?
– Any joint pain in upper limb, backache?
– Any known illness in child / family?
– Possibility of NAI
Examination:
– Febrile / afebrile? Systemically unwell?
– Any bruising, pallor? Lethargic?
– Rash (e.g. HSP)
– P-GALS assessment*
– Weight-bearing possible?
– Observe gait and balance
able to run, walk on tiptoes, hop?
– Joint exam– any swelling, redness, warmth
– Joint movements–
full range, pain free & symmetrical?
– Hips – including int/ ext rotation
– Examine spine, knees and small joints in hands/ feet
– Tone, Power, tendon reflexes, plantars?
– Lymphadenopathy? Hepatospleenomegaly?
– Groin swelling? Testicular swelling in boys?
Red Flags in a Limping Child:
– Fever
– Young child with suspected NAI
– Limping for over 2 weeks
– Pallor, bruising tiredness
– Backache, night sweats
– Lymphadenopathy,
Hepatospleenomegaly
– Focal neurological abnormality
– Known Sickle cell dis,
immunocompromise
– More than 1 joint affected
Investigations:
None if suspecting irritable hip
(see management prompts)
– Safety net advice & review in 72 hours
Febrile/ red flags/ systemically unwell:
– FBC, U&E, CRP, Bld culture
– Xray Pelvis
(AP if <8y; AP & Frog leg if >8y)
– Xray of another joint if affected
– Orthopaedic referral for urgent
joint aspiration before antibiotics
Targeted tests for other causes
– USS abdomen & Pelvis
– MRI of joint/ abdomen/ pelvis
Management:
Depends on likely cause
Transient synovitis in 3 – 8y age:
– Post viral, short duration limp <3d
– systemically well, no red flags
– pain localised to hip, rarely knee
– May have mild effusion in joint
– resolves in 10 – 14 days
– Offer pain relief & review in 3d
Septic arthritis:
– Can be a subtle presentation
– Can rapidly destroy a joint
– Urgent joint aspiration before antibiotics
Perthes disease:
– Avascular necrosis of femoral head
– Age 4 – 10 years
– Xray shows flat irregular femoral head with increased joint space
SUFE:
– Obese (boys>girls)
– Peripubertal age
– Affected leg externally rotated
– Xray Frog-Lateral view
femoral epiphysis slipped
Other potentially serious diagnosis
