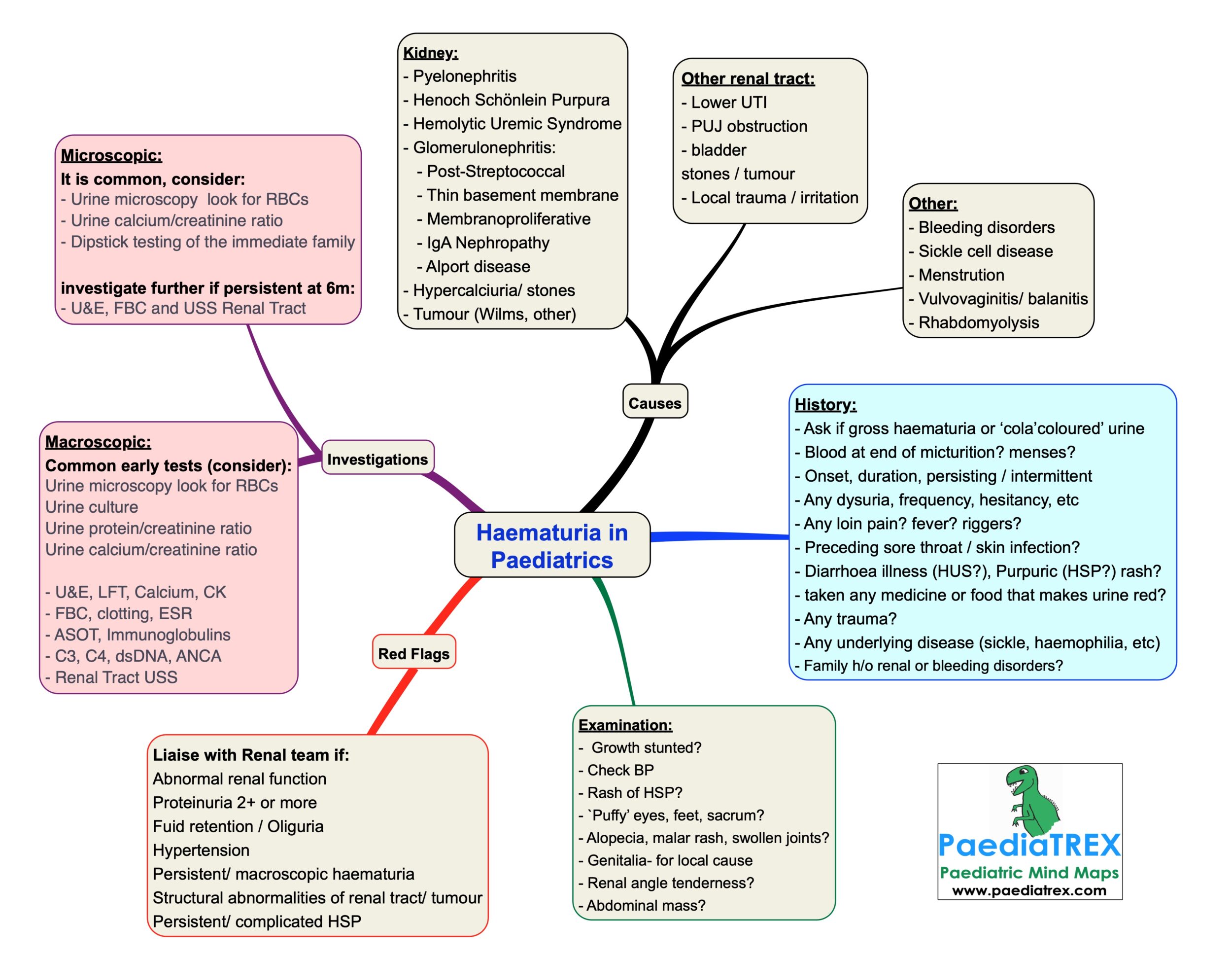
Haematuria in children
Renal causes:
– Pyelonephritis
– Henoch Schönlein Purpura
– Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
– Glomerulonephritis:
– Post-Streptococcal
– Thin basement membrane
– Membranoproliferative
– IgA Nephropathy
– Alport disease
– Hypercalciuria/ stones
– Tumour (Wilms, other)
Other renal tract:
– Lower UTI
– PUJ obstruction
– bladder stones / tumour
– Local trauma / irritation
Other causes:
– Bleeding disorders
– Sickle cell disease
– Menstrution
– Vulvovaginitis/ balanitis
– Rhabdomyolysis
History:
– Ask if gross haematuria or ‘cola’coloured’ urine
– Blood at end of micturition? menses?
– Onset, duration, persisting / intermittent
– Any dysuria, frequency, hesitancy, etc
– Any loin pain? fever? riggers?
– Preceding sore throat / skin infection?
– Diarrhoea illness (HUS?), Purpuric (HSP?) rash?
– taken any medicine or food that makes urine red?
– Any trauma?
– Any underlying disease (sickle, haemophilia, etc)
– Family h/o renal or bleeding disorders?
Examination:
– Growth stunted?
– Check BP
– Rash of HSP?
– `Puffy’ eyes, feet, sacrum?
– Alopecia, malar rash, swollen joints?
– Genitalia- for local cause
– Renal angle tenderness?
– Abdominal mass?
Investigations:
Microscopic haematuria is common, consider:
– Urine microscopy look for RBCs
– Urine calcium/creatinine ratio
– Dipstick testing of the immediate family
investigate further if persistent at 6m:
– U&E, FBC and USS Renal Tract
Macroscopic haematuria, common early tests:
Urine microscopy look for RBCs
Urine culture
Urine protein/creatinine ratio
Urine calcium/creatinine ratio
– U&E, LFT, Calcium, CK
– FBC, clotting, ESR
– ASOT, Immunoglobulins
– C3, C4, dsDNA, ANCA
– Renal Tract USS
Liaise with Renal team if:
Abnormal renal function
Proteinuria 2+ or more
Fuid retention / Oliguria
Hypertension
Persistent/ macroscopic haematuria
Structural abnormalities of renal tract/ tumour
Persistent/ complicated HSP
