Syncope in children
Syncope (fainting) is a brief loss of consciousness and loss of postural tone with spontaneous recovery.
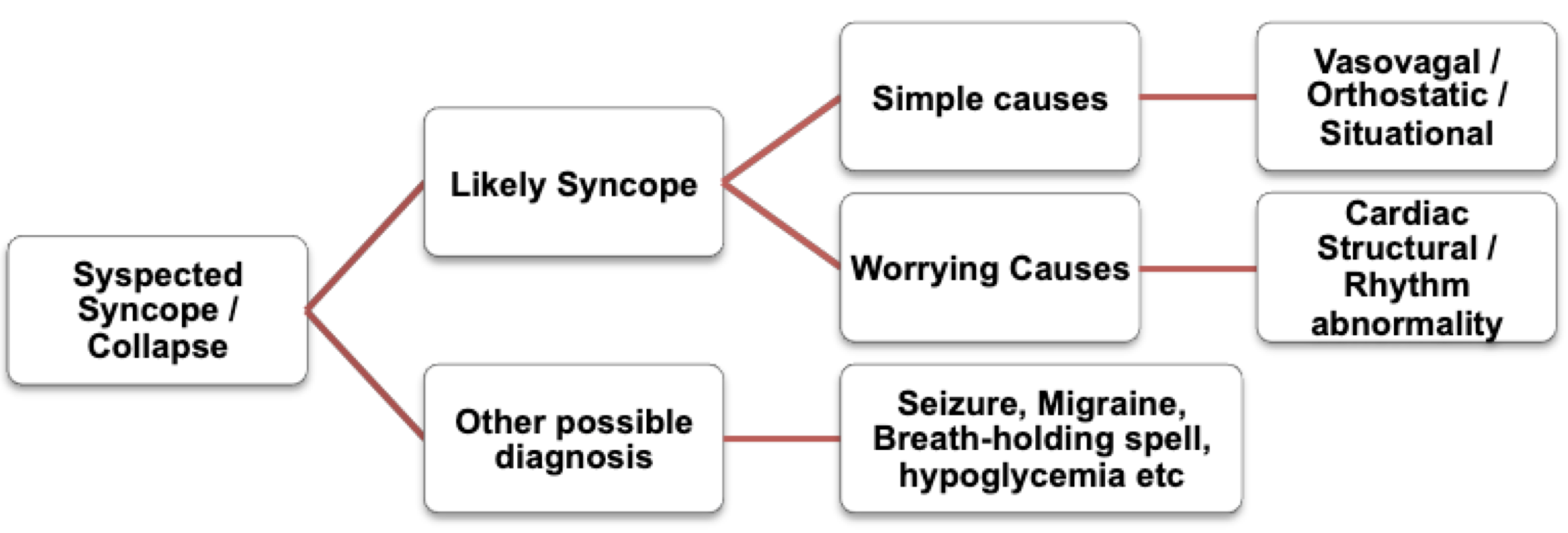
Most cases are benign- vasovagal or hypotension related
Hence, your main task is to differentiate a simple faint from other causes primarily with a good history, examination and ECG
Simple causes
1.Vasovagal: prodrome of nausea & sweating; triggered by pain, anxiety, prolonged standing or a warm place
2.Orthostatic: triggered by dehydration, alcohol & BP medications
3.Situational: micturition, cough, defecation; or by carotid sinus pressure
Worrying causes
1.Cardiac Structural problems: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Aortic Stenosis, etc
2.Cardiac rhythm abnormalities: VT, WPW syndrome, Congenital long QTc syndrome, Heart block, etc
History:
– Sequence of events (before, during & after episode)
– Describe posture, duration of LOC
– Any stiffness / jerking?
– Contributory factors?
– Associated palpitations, chest pain or breathlessness?
– PMH
– Medications (hypotensive)
– Family h/o cardiac issues
Examination:
– Pulse rate, rhythm
– Blood pressure, lying & standing
– Hydration status
– Focussed Cardiac and Neurological exam
– Check BM & ECG
Red Flags in syncope:
– With exercise
– With palpitations or chest pain
– No warning or prodrome
– Known cardiac problem
– F/H/O arrhythmia or early death
Key ECG changes to look for:
PR interval
short PR and delta wave?… WPW syndrome
long PR?… type II or type-III heart block
QTc interval prolonged?
Congenital prolonged QTc syndromes
Any recent medication prolonging QTc?
QRS complexes
increased tall R on V1 or deep S on V5, V6…. is there RV hypertrophy?… HOCM
Tachy with wide QRS/ ventricular pre-excitation/ ectopics?……. VT, BBB
ST / T wave changes … acute myocarditis
Management of simple faints:
– Explanation about nature of episodes & reassurance
– Identifying / avoiding precipitants
– Self-management of symptoms- patients should sit or lie down if recognising early warnings of fainting; will also prevent injuries
– Maintain good hydration, avoid skipping meals & adequate salt in diet
What specialist tests may be considered?
– Holter ECG (24-hour tape)
– ECHO
– Exercise ECG testing / stress test
– Tilt-table testing
