Paediatric Hypertension
Elevated blood pressure is an uncommon finding in children, so be certain this is not due to pain, discomfort, upset or anxious child or wrong BP cuff.
Differentials include:
– Brain tumour
– Intracerebral hemorrhage
– Meningo-encephalitis
– Stroke
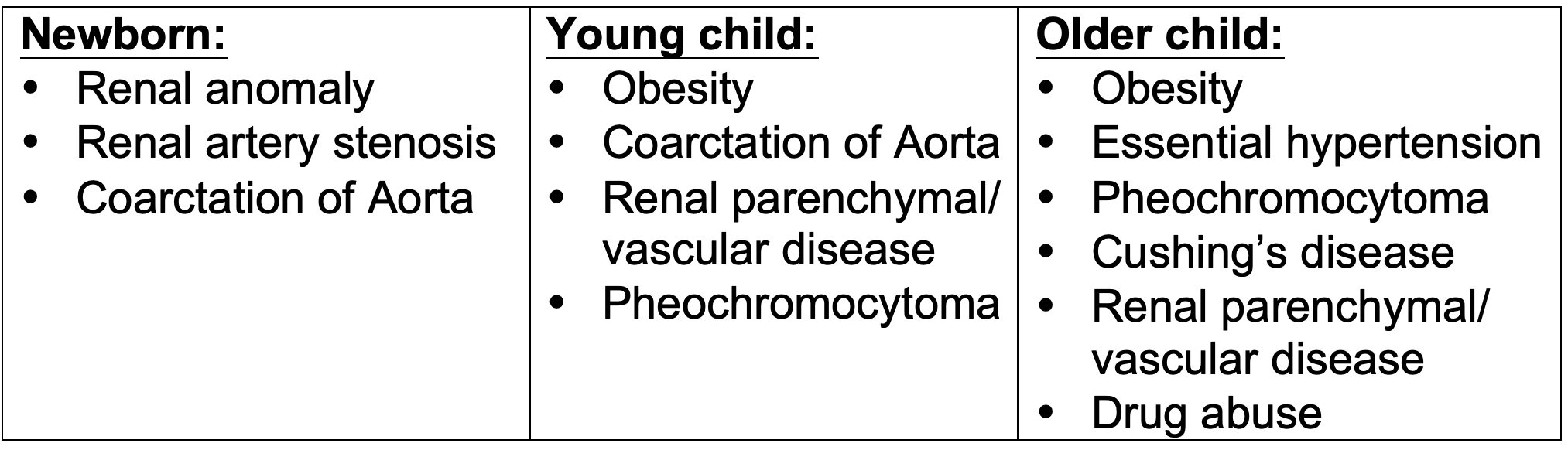
Common causes of hypertension are:
History:
– Any headaches, vomiting, nose bleeds, blurred vision
– Excess tiredness, sleep issues or snoring
– Episodes of flushing, palpitation, sweating?
– Past h/o UTI, known renal/ cardiac condition, Diabetes
– Any medications (e.g. Steroids) or substance abuse
– Family h/o hypertension, heart disease,
stroke, cholesterol issues or known renal disease
Examination:
– Acutely unwell? Raised ICP?
encephalopathy, seizures, heart failure?
– Any acute pain/ distress/ illness?
– Measure 4-limb BP (is UL BP higher by 10mmHg?)
check femoral pulse (infants, toddlers)
– Goitre/ Facial palsy/ Squint?
– Features of Williams synd, NF1, Cushings disease?
– Short stature (chr renal dis)?
– Obesity (generalised/ truncal), buffalo hump,
stretch marks, acanthosis
– Any abdominal/ renal mass?
– Any fundus changes of chronic HT or raised ICP
Management principles:
– Treat any underlying cause
– Reduce BMI if obese
– Reduce dietary salt
– Regular exercise
Medications required if:
– Markedly high BP
– Symptomatic hypertension
– Secondary HT with
end organ damage
Reduce BP percentiles to
<90% for all
<75% if chr renal dis
Investigations:
In all cases:
– U&E, Bone profile, TSH
– FBC (anaemia of chr dis)
– Fasting glucose, lipids
– Urinanalysis- dip (RBC, prot) & microscopy
– USS Abdo, Kidneys and Renal tract
(consider doppler renal vessels)
– ECHO
Selectively:
– Glomerulonephritis screen
(C3, C4, ASOT)
– Plasma Renin, Aldosterone, Cortisol
– Urinary Catecholamines
– Urine Albumin/ Creat ratio
– DMSA scan
– CT / MRI Head
– CXR
– ECG
– Sleep SaO2 for OSA
Common drugs:
– Captopril (ACEI)
– Atenolol (beta-blocker)
– Nifedipine (Ca- blocker)
– Frusemide (Diuretic)
– IV Labetolol/ Nitroprusside
